The Project
The project aims to combine the efforts of Chinese and Bulgarian researchers to develop new knowledge and advanced tools for modeling and assessment of flood hazard in urbanized coastal and estuarine areas.
The numerical modelling of flooding in large coastal city areas with complex topography (and bathymetry of estuaries and seas) frequently requires significant efforts to build relevant digital elevation models, as well as further model ‘reduction’ and ‘optimisation’ in order to achieve expedient conclusions.
The Composite Modelling (CM) that integrates physical modelling, numerical simulations, verified by prototype / field measurement data, is a reliable method to improve modelling and forecast, and provide relevant information for flood risk management. These elements can essentially complement each other – physical model provides verification data for numerical models, while model simulations provide the continuum information to bridge the gaps in field data, etc. This approach is applicable for assessment of coastal flooding due to storm surges and wave action, as well as for flash floods in rivers, but most of all - for the worst combination of these two in coastal estuarine (city) areas.
The project will continue previous joint efforts of Bulgarian and Chinese scientists to study various “composite” modelling techniques for simulation, prediction and analysis of risk of flooding.
Physical model tests and field measurements will be carried out independently by the Chinese and Bulgarian researchers, while the numerical simulations will be carried out as a joint effort.
Main scientific challenges that will be addressed:
- Study and analysis: understanding hydrology, hydrodynamics and environmental aspects of urban flooding;
- Develop/ Improve Existing Numerical and Physical Modelling tools
- Proper exchange of information between numerical and physical models when applying composite models of flooding; Problems with different spatial scales; modelling the far field by numerical modelling, and the near-field with physical modeling;
- Appropriate use of high-generation numerical models of the type 2D/3D free surface flow on unstructured meshes (MIKE), or “Navier-Stokes Solvers, Volume-of-fluid (VOF) models,
- Uncertainty analysis: possible multiplication of errors from physical to numerical model, and vice versa.
Suggested way of cooperation includes independent work (by each side) on the selected topic; exchange of data, and results, on their developments relevant to the project topic; exchange of researchers for short time visits from 7 to 14 days (e.g. 2 persons from/to each side during each project year); joint performance of pilot test, calibration, verification of the tools within the project developments; organization of a scientific seminar to discuss achievements of both sides, exchange knowledge and experience; preparation of joint scientific publication(s) on the subject of the project.
The results of the project will include developments of :
- New knowledge on hydrology, hydrodynamics and environmental aspects of urban flooding
- Improved numerical and physical modeling tools and methods for simulation of flood in urbanized areas
- Practical recommendations for application of developed methods and tools
- Scientific publications
Project results
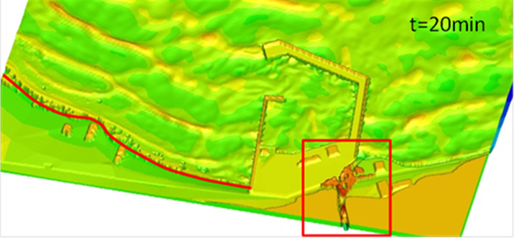
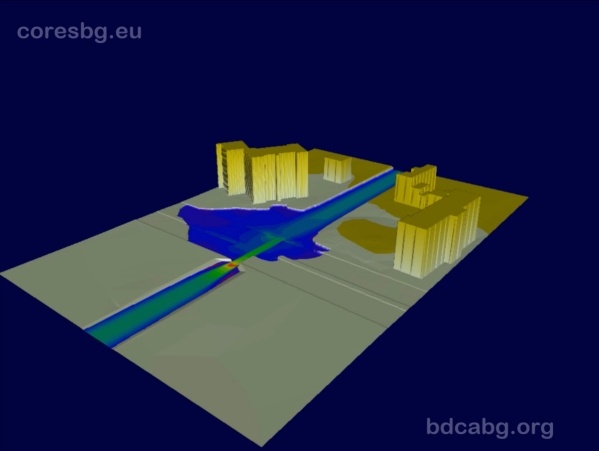
The aim of the project was to explore in case studies the comparatively new “composite” approach to modeling coastal floods that combines the use of various well-established modeling tools: modern numerical models in combination with physical modeling and validation with data from field measurements. Within the project an exchange of scientists and scientific information and acquired new knowledge on the specificity of the complex flood and the modeling of the inherent hydrodynamic processes was carried out. Numerical modeling of flood has been carried out in a urbanized coastal area of Asparuhovo – Karantina beach in Varna region, caused by river overflow and sea storm, For these purpose a detailed digital elevation model of the complicated terrain was developed. Different software programs were used for numerical modeling (MIKE FLOOD, SWASH), and results were compared. Modeling (numerical and physical) of the wave overtopping of a protective dike was carried out with simultaneous effects of sea level rise and extreme waves in the area of the city of Beilun, China.
The results were analyzed and included in two papers presented at two international forums (the"BlackSea'2018" Conference in Varna, https://fccvarna.bg/event/black-sea-2018, and the International Symposium "ISFF'2018" in Casablanca, Morocco, http://www.isff2018.com/.
Within the framework of the project in 2018, a bilateral scientific seminar with the participation of Chinese scientists from the team was held at the BSHC in Varna. The presentations presented by the Chinese and Bulgarian researchers at the seminar in Varna are collected in a properly designed book.
Physical model of protective dike near Beilun city, China

Numerical modeling of flood with MIKE FLOOD (Asparuhovo-Karantina coastal area, Bulgaria)
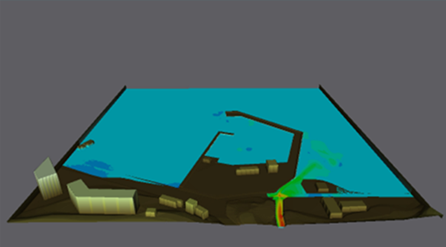
Numerical modeling of flood with SWASH (Asparuhovo-Karantina coastal area, Bulgaria)